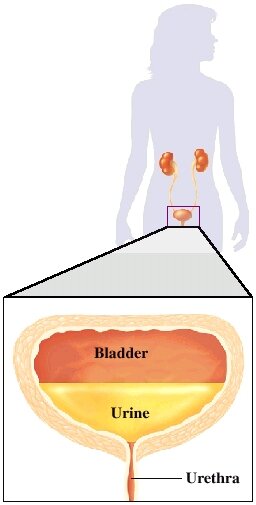
 The urinary tract helps to get rid of urine. The lower part of the urinary tract includes the bladder and the urethra. The bladder stores urine until it is ready to be released. The urethra is a canal that carries the urine out of the body. The urinary flow is monitered by a muscles around the opening of the bladder called the sphincter. Signals from the brain tell the sphincter when to relax and the bladder when to contract to let the urine flow out of the body.
The urinary tract helps to get rid of urine. The lower part of the urinary tract includes the bladder and the urethra. The bladder stores urine until it is ready to be released. The urethra is a canal that carries the urine out of the body. The urinary flow is monitered by a muscles around the opening of the bladder called the sphincter. Signals from the brain tell the sphincter when to relax and the bladder when to contract to let the urine flow out of the body.
WHY DO?I NEED A URODYNAMICS STUDY?
A urodynamic study is a series of tests that gives your doctor a detailed look at the function of the bladder and urethra. These tests help to discover treatment options for incontinent, not voiding bladder completely, frequent urination, weak urine stream, or persistant urinary tract infection.?
The study may take place in the doctor's office, clinic, or hospital. Depending on which tests are being done, the study may take up to an hour or more.
| Uroflowmetry | This test measures the amount and speed of urine you release from the bladder. A computer will determine the urine flow over time. The amount of urine remaining in the bladder may also be measured. |
| Cystometry | This test evaluates how much the bladder can hold, how strong the bladder muscle is, and how well the signals work that tell you when your bladder is full. |
| Electromyogram | This test evaluate the muscle control for urination. |
| Pressure Flow | This test measures the pressure and flow of urine out of the bladder. A probe in the urethra will measure pressure during urination. |
| Video Cystourethrography | This test takes video pictures of urine flow through urinary tract. |
?
WHAT TESTS WILL BE PERFORMED?
Some people have problems storing or voiding urine. To evaluate these problems doctors perform a series of tests that give a detailed look at the functions of your bladder and urethra.
